How Does the Moon Affect Tides?
There is a lot to understand about how weather and the sun and moon will affect the sea. In terms of tides, the moon does govern them. The moon’s gravitational pull is the main force affecting high and low tide.
Understanding how the moon’s gravitational pull affects ocean tides is important. Knowing when to expect low and high tide can go a long way to boating safety. Not to mention understanding spring tides, neap tides, and the whole tide cycle.
Let’s take a look at the forces behind how the moon affects the tides. And how that can affect you when you’re on the ocean.
What is the Tide?
Everyone has heard of the ebb and flow of the tide. It comes in, it goes out, right? Not so fast. The old school understanding of how tides work is not exactly scientific. While it certainly looks like the tide creeps in then out again, there is more going on. Gravity is the main force at work here. It causes the sea level to rise and fall.
Tide is actually a vertical movement of water. It goes up and down, not forward and backward. When you think of water flowing in and out, that’s actually current. Current floods in which makes the tide rise. As it ebbs out, the tides fall. The two forces work together to make what we think of as the tide happen.
What Does the Tide Do?
The up and down movement of the tide is significant for boaters. After all, your boat is on the water. If the water level rises, and your boat is moored, that’s important. How you dock your boat, and the length of line you use, is relevant to the tide. The shallower the harbor, the more important this becomes.
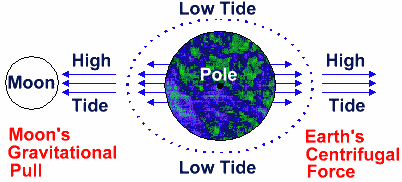
How Does the Moon’s Gravity Affect the Earth?
The moon and sun work together in a tidal cycle. On any given day there are two high tides and two low tides. In between low and high tide the current continues to flow. The moon’s gravity is the force behind this
The moon’s gravitational pull acts on the earth. This force of gravity creates tidal pull. The gravitational pull causes the earth to bulge on the side closest to the moon. It also bulges on the other side of the earth. As a result, oceans rise. The bulging areas experience high tides. The other areas experience low.
You may wonder how the side closest to the moon bulges but the other side of the earth does also. Think of the earth like a ball. The gravitational pull makes it squish in the middle.
Because of the influence of coastlines, tidal force can be inconsistent. The force in one part of the world may be significant while it is barely noticeable somewhere else. The gravitational pull will be even, but the effect is not. Irregular coastlines contribute to this.
How Much Time Is There Between Tides?
You have roughly six hours between high tide and low tide every day. This is the lunar tide cycle. The cycle will repeat about 50 minutes later after day. That means you can roughly calculate when the tides come in every day. If today’s low tide is at 0700 hours, tomorrow’s low tide will be around 0750 hours.
This is because, although the moon rotates the earth, it is the Earth’s rotation that is important. A full moon takes roughly a month to rotate around the earth to a new full moon. But, as you know, a full rotation of the Earth takes one day. To get the moon back to the same place in the sky each day takes roughly 24 hours and 50 minutes. You can call this one tidal day.
What is the Range of Tide?
The difference between high tide and low tide is known as the range of tide. As an example, the water level in harbor may have a depth of 20 feet at high tide. At low tide it could go down to 18 feet. This difference means that the range of tide is 2 feet. The current will change with the tides as well.
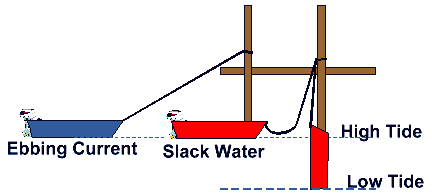
When the tide is rising the current you experience is flooding current
When the tide is falling the current you experience is ebbing current
At its highest or lowest points, there is no current involved with the tide. This is called slack water. An ebbing current will pull your boat away from the where you have it moored. In a flooding current it may be pushed towards shore or the dock.
What is a Spring Tide?
Both the sun and moon affect the tide. Because the sun is so far from Earth, its effect on the tide is less noticeable. However, when the sun and moon are in alignment with each other, the effect is more noticeable. This results in higher high tides and lower low tides. It is the product of lunar tides and solar tides working together. These are also known as spring tides.
Spring tides happen during a new moon or a full moon. These spring tides are stronger but they only happen every two weeks.
What is a Neap Tide?
The opposite of spring tides are neap tides. Neap tides happen when lunar tides and solar tides are at odds. If the sun and moon are at right angles you’ll have a neap tide. Basically neap tides are when the sun’s pull and moon’s gravitational pull cancel each other out. You will have lower high tides and higher low tides as a result. Neap tides occur as often as spring tides.
What Else Affects Tides?
Weather systems can have an affect on tides. Strong winds will give the appearance of causing a more significant high tide. The tide itself is not actually affected by weather in this way, however. The end result is still the same. Winds can push a high tide and flooding current further inland. Likewise, onshore winds can push a low tide and ebbing current further out. These can seem to have a stronger effect than the moon’s gravity.
High and low pressure systems can also have an effect on how tides work. They can lead to unexpected variation in sea levels. Tides can end up being much higher or much lower than predicted.
How Do I Track the Tide?
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration can provide information about the tides. This includes water levels, times, and predictions. You can also download apps for your phone that can help you determine things like;
- Time of high tide
- Time of low tide
- Tide range
- Water depths at high tide and low tide
- Times of slack water
You can get access to tide charts for any region of the country. It is good to familiarize yourself with the tidal times and depths. Do this before heading out on any boat trip. That way you can avoid unexpected surprises.
Use the Rule of Twelfths
If you do not have access to tidal charts, you can use the rule of twelfths. This is a handy approximation to help you navigate tides. It works with some basic math.
It takes about six hours to go from low tide to high tide. Then another six hours to go back down to low tide, give or take. You can divide the time between tides into 1/12 units. Every hour after low tide, the tide will rise by 1/12th of the tidal range. Then 2/12th. Then 3/12th and so on. After high tide is reached, it goes in reverse. This will give you a rough approximation of water levels and when to expect tidal activity. Typically, hour three and four have the most tidal activity. For five and six it gears down again.
This is just a rough approximation, of course. Ocean tides do not work on a precise hourly schedule. It’s actually closer to 12 hours and 25 minutes for every lunar high tide. This is due to the tidal day we mentioned earlier. It’s 24 hours and 50 minutes. Still, if you are on your boat and looking for a good estimate, this will work.
What Does the Tide Mean to Boaters?
When you have a boat, understanding tides is essential. The effect of the tide can be easily overlooked. But you may also regret not understanding how the tide works. For instance, these things can be affected by the tide;
- The length of dock lines and anchor chains
- How long you can stay safely anchored in one spot. More than one boater has discovered themselves beached at low tide. Likewise, high tide could send your boat adrift if it was not properly anchored.
- Clearance for the keel of your boat over shoals or debris. You don’t want to run aground.
- Clearance for your boat under a bridge
- Your ability to navigate channels and inlets. This affects not just tidal depths, but also current. You may not be able to sail against some currents in some channels.